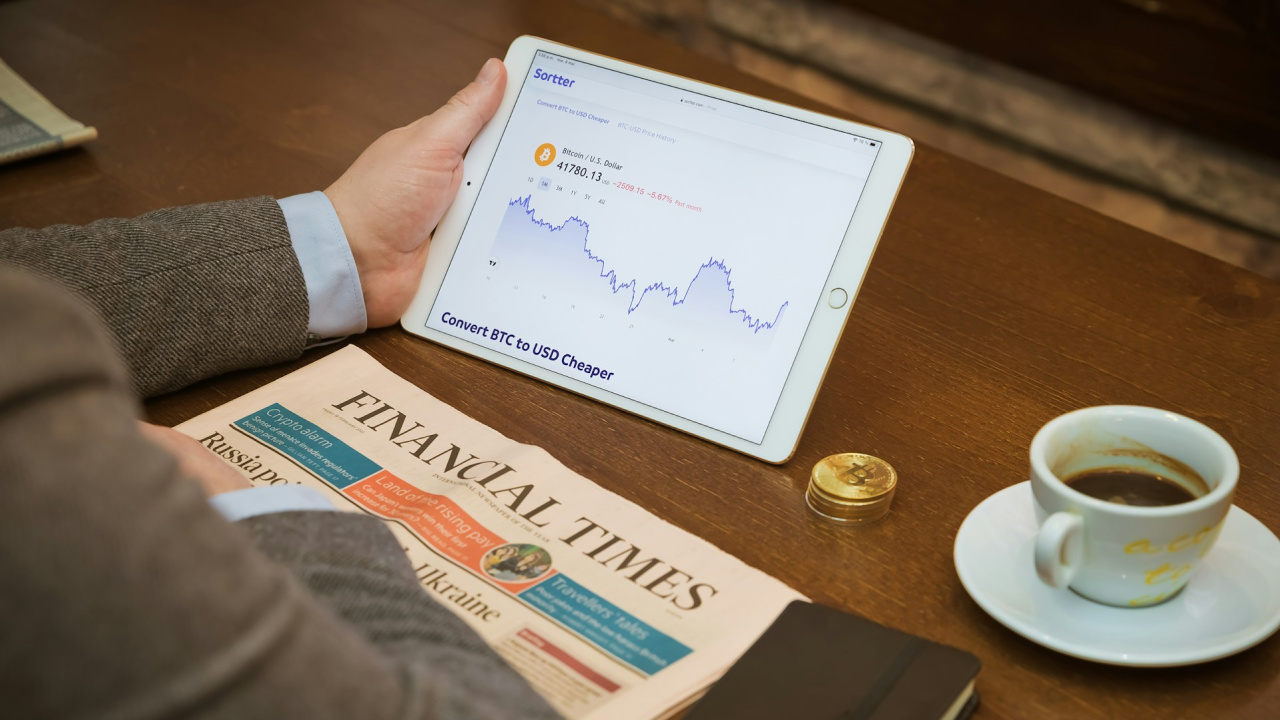
The current portfolio must take into consideration that the world has changed, and with it, the investment strategies too. How to move?
Investing today means conceiving and building an investment portfolio as a tool that can withstand external shocks without capitulating: in two words, it should be diversified. Until a few years ago, there were precise, shared guidelines used as a reference in the financial planning process. Today, the situation has changed. What to do?
Why should investment strategies be rethought?
The world has completely changed in the last 5 years. Since at least 2020, we have been witnessing a series of events that are overturning the established order to which we were accustomed.
Everything we took for granted and considered immutable regarding military interventions, geopolitical alliances and economic agreements is evolving towards a new arrangement. To put it briefly, we might have reached the end of the line for the phase of absolute globalisation, which began with the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991.
The basics: where does it all start?
We could place the starting point of this apparent change process in the period between 2018 and 2022. Over the past five years, three historical events contributed to changes in past balances: the trade war between the United States and China, the COVID-19 pandemic, and the Russian invasion of Ukraine.
The trade war between the United States and China
In March 2018, in fact, the American administration led by Donald Trump imposed 25% tariffs on about $50 billion in goods imported from China, following a report by Robert Lighthizer, US Trade Representative, that denounced certain unfair trade practices by the People’s Republic. The latter, naturally, responded and imposed tariffs on 128 strategic American products.
This initiated a trade war that revealed the criticalities of a super-connected system, perhaps too dependent on Chinese manufacturing: the deterioration of relations coincided with the supply chain crisis. Furthermore, the clash of tones between the two leading world powers, which embodied – and still embody – two opposing economic and political systems, contributed to the re-emergence of polarisation dynamics typical of past eras, especially the Cold War period. Chancelleries around the world returned to asking themselves an old question: which side to take? United States or China?
The Covid-19 pandemic
We arrive at 2020: in February, it is an epidemic, in Jun, it is a pandemic. COVID-19 blocks the world. Leaving iconography aside, the prolonged lockdown exacerbated supply chain problems that had emerged over the previous two years, besides immobilising national production: as Statista reports, the global Gross Domestic Product (GDP) contracted by 3.4% or, in dollars, by 2 trillion. Obviously, financial markets also took the hit: the Dow Jones (DJI) – the most important index in the world – lost about 35% from mid-February to mid-March. In the same period, Bitcoin fell from $9,970 to $5,300, a 46.6% decline.
As we know, both GDP and markets recovered from the blow with a sensational rebound: from that moment to today, the DJI has gained 144%, the S&P500 187% and Bitcoin 2,100% (a percentage that rises to 3,130% if we consider the ATH at $126,000).
Info on the first vaccines began to circulate, collective panic reduced, and confidence returned to acceptable levels. But above all, governments around the world flooded their respective economies with an infinite amount of liquidity and fiscal stimuli.
Taking into consideration only the three leading economic powers, the United States ratified the CARES Act for 2.2 trillion dollars, China approved a plan for 3.6 trillion yuan (about 500 billion dollars) and the European Union put in place a series of interventions – the most important being the PEPP (Pandemic Emergency Purchase Program) and NextGenerationEU – for a total of almost 2 trillion dollars. To this, one must add the various economic policy measures aimed at reducing the cost of money, such as low interest rates, quantitative easing, and so on.
Today, in the US alone, the M2 Money Stock, i.e., the total quantity of dollars in circulation in the real economy, has reached 22 trillion, up from 15.4 trillion in February 2020. At this point, a serious problem began to spread through the corridors of central banks worldwide. A problem to which we devote a lot of time: inflation. But the “best was yet to come”.
The Russo-Ukrainian War
February 2022: Putin’s Russia invades Ukraine; it is the perfect storm. Passing over the humanitarian issue, which, whilst central and very grave, is not the target of our article, the Russo-Ukrainian War is considered the decisive catalyst: its outbreak coincides with the conclusion of that period of apparent peace and free movement of goods made possible by American-style globalisation.
Russia and Ukraine were vital nodes in global trade before the war. Suffice it to say that, together, the two countries accounted for about 30% of global exports of low-cost wheat and cereals, while Russia was one of the leading European suppliers of gas and held a prime position in the worldwide supply of fertilisers, necessary for agriculture.
With the war, all this ceases to exist. The conversion of the Russian and Ukrainian economies to war economies creates significant structural difficulties in both countries, as they no longer produce at pre-conflict levels and fail to meet demand. Furthermore, supply chains are now politicised: before, one bought where it was convenient; now, one tries to buy from allies, even at higher prices (sanctioning enemies). Finally, the damage and strategic blockades of logistics infrastructure – such as the Ukrainian Black Sea ports– constitute a permanent impediment to resource access.
The current state of affairs
Some of the pillars that made the creation of an interconnected and efficient global economy possible have definitively collapsed, such as the constant availability of low-cost raw materials, international transport at negligible costs and logistics security, i.e., the certainty of receiving goods without interruptions or delays. In a few words, it is the end of the JIT (Just-In-Time) model.
The paradigm has changed. Priority is security of supply, not efficiency, also by virtue of the politicisation of supply chains mentioned earlier. The most recent example is China’s decision to limit access to rare earths on a discretionary basis, to which Trump responded by imposing 100% tariffs. The emergency “subsided” in a few days, but these tensions led to liquidations worth billions of dollars.
Inflation becomes a persistent problem insofar as it is systemic, also because it is imported, i.e., upstream: if before the baker sold bread at five. He paid bills at two and flour at 1, keeping another 1 for himself. Now he pays bills at three because he can no longer avail himself of low-cost Russian gas, flour at two, and is forced to raise the final price to earn 1.
In Italy, for example, from 2004 to 2021, prices grew at a slow and steady pace: as Pagella Politica reports, over 17 years, the increase was 28%, with an annual average of 1.5%. Only in 2022, however, the general price index rose by 11%, then fell to 8% in 2023 and returned to 2% in 2024. Put another way, to use the words of the research authors, “little less than half of the increase accumulated in twenty years was therefore concentrated in just three years”.
Now that we have a clear picture of the transformations underway and their causes, it is time to answer the central question.
Investing today: what is necessary to consider?
In the current world, the primary variable to consider when building a portfolio, as we have seen, is high inflation, now a constituent element of our economic system.
In the past, in the world of investments, one “rule” in particular influenced the art of diversification for a very long time: the famous 60/40 portfolio. In two words, this established that the perfect portfolio should be composed of 60% equities and 40% bonds.
The reason is simple: the negative correlation between the two asset classes. This is because, in the “old world”, during periods of economic growth, shares performed better than bonds and, conversely, in moments of recession, bonds compensated for the losses of shares. In this historical moment, however, the 60/40 portfolio is no longer valid.
Shares and bonds are increasingly correlated, and the latter are reportedly gradually losing their status as havens – safe havens to preserve capital – in favour of other assets.
Inflation, in fact, constitutes a big problem for bonds, for at least two reasons: firstly, investors holding them receive fixed interests, or coupons, in return, which are proving unsuitable for protecting capital from the loss of purchasing power; secondly, with such entrenched inflation, central banks are forced to keep rates high causing, ultimately, a descent in the value of bonds.
To give an example, let’s take TLT, an ETF that allows investors to expose themselves to US government bonds with maturities exceeding 20 years: from its launch in 2002 until 2020, TLT performed exceptionally well, growing slowly but steadily, scoring approximately +100%, with the ATH precisely in the first week of March 2020. From that moment, however, a sensational decline began: from April 2020 to today, this ETF has lost more than 40%. If you had invested in TLT at day zero in 2002, you would have earned a scant 10% today.
Where to invest money today?
Naturally, before starting this section, it is necessary to remember that what you will read here is not investment recommendations or financial advice, but only considerations stemming from reading expert opinions.
That said, an interesting analysis comes from within the walls of Goldman Sachs, more precisely from the section dedicated to market analysis, Goldman Sachs Research. In the study, consistent with what has been written so far, one reads that a strategy of “passive acceptance”, such as investment in global indices (World Portfolio), might no longer be so functional. On the contrary, the so-called Strategic Tilting might be more suitable, literally “Strategic Inclination”, i.e., the almost active management of one’s portfolio to safeguard oneself from current vulnerabilities – inflation primarily.
Doing Strategic Tilting, therefore, means diversifying but in a conscious way. A simple metaphor that helps us understand the concept comes from the culinary field.
Imagine wanting to prepare your favourite cake, the one grandmother taught you as a child when you came home from school. Well, grandmother’s recipe, with the quantities and cooking times, worked perfectly with grandmother’s home oven. Your oven, however, heats up more.
It is a variable you must consider; otherwise, the cake will turn out very different and perhaps burnt. Therefore, you weigh the ingredients so that the problem with your oven is minimised: of the 500 grams of flour, you remove 50 grams and replace them with another 50 grams of starch to soften.
Now, your grandmother’s classic recipe is the global index, which worked perfectly with the old oven (the “old world”). The new oven, however, is more powerful – the macroeconomic context is different, and inflation is structural. For this reason, you changed the ingredients or, in financial terms, you actively managed – but not too much – your allocations, so that the cake (the investment) can perform at its best. This is Strategic Tilting.
The analysis, in this regard, identifies five macro-areas to mitigate risks.
- Protection against inflation: the 60/40 portfolio, as we have seen, struggles to preserve capital amid the inexorable erosion of inflation. For this reason, experts from the Research section explain, it is necessary to rebalance it by increasing exposure to tangible assets – real estate, raw materials and natural resources – and gold. In this regard, the Chief Information Officer of Morgan Stanley, Mike Wilson, believes that the noble metal should weigh at least 20%.
- Protection from the end of United States dominance: new powers challenge US leadership daily, with China in the lead. For this reason, non-US shares deserve greater attention when planning a medium- to long-term strategy.
- Protection from the weak dollar (Pt. 1): the cause and at the same time the consequence of the second point. If the United States lost leadership, the dollar would cease to be the centre of world finance. The argument also holds in reverse: if dedollarisation gained strength, the USA would cede command. In light of this, emerging markets, which have historically been negatively correlated with the dollar, could represent a lifeline.
- Protection from the weak dollar (Pt 2): To protect oneself from this phenomenon, it also makes sense to reduce exposure in USD and start looking towards other shores, such as the euro or the Swiss franc.
- Protection against volatility: US Tech shares, which carry significant weight in the S&P 500 and Nasdaq, are highly volatile. For example, NVIDIA’s quarterly reports moved the stock by 8% in one day – from +5% to -3% in one session. In this sense, low-volatility shares can attenuate shocks: utilities (companies that provide public utility services) and healthcare (public health).
Have strategies changed?
To answer the opening question: yes, strategies have changed. New investment paradigms, to be in step with the times, should incorporate parameters that can no longer be ignored. Many schools of thought propose different approaches. The common denominator, however, is one: the 60/40 portfolio, the maximum expression of a world now passed, might no longer be the cure for all ills.

Sign up to Young Platform