What is Young Platform Step and how does it work? Discover the app that lets you learn all about the crypto world by playing!
With Young Platform Step you can discover what the crypto world is and how it works in the easiest and most fun way: collect experience points and level up to get the YNG token!
But what is it? It’s the token of the Young Platform ecosystem, with real value in the market. On Step you can set aside your first YNG tokens and get lots of free resources to learn the basics of the crypto world, step by step!
How does a blockchain work? What is Bitcoin for? What are NFTs? Step gets down to business and answers all your questions, simply and clearly. But it doesn’t end there! Once you’ve got your first YNGs, you can transfer them to the Young Platform exchange where you can take advantage of the crypto industry’s leading services with an extra edge. So find out what Young Platform Step is and how it works and all the games available!
What games are there on Step?
There are several features on the app to gain experience points (XP) and level up. Let’s see what each Young Platform Step game is and how it works:
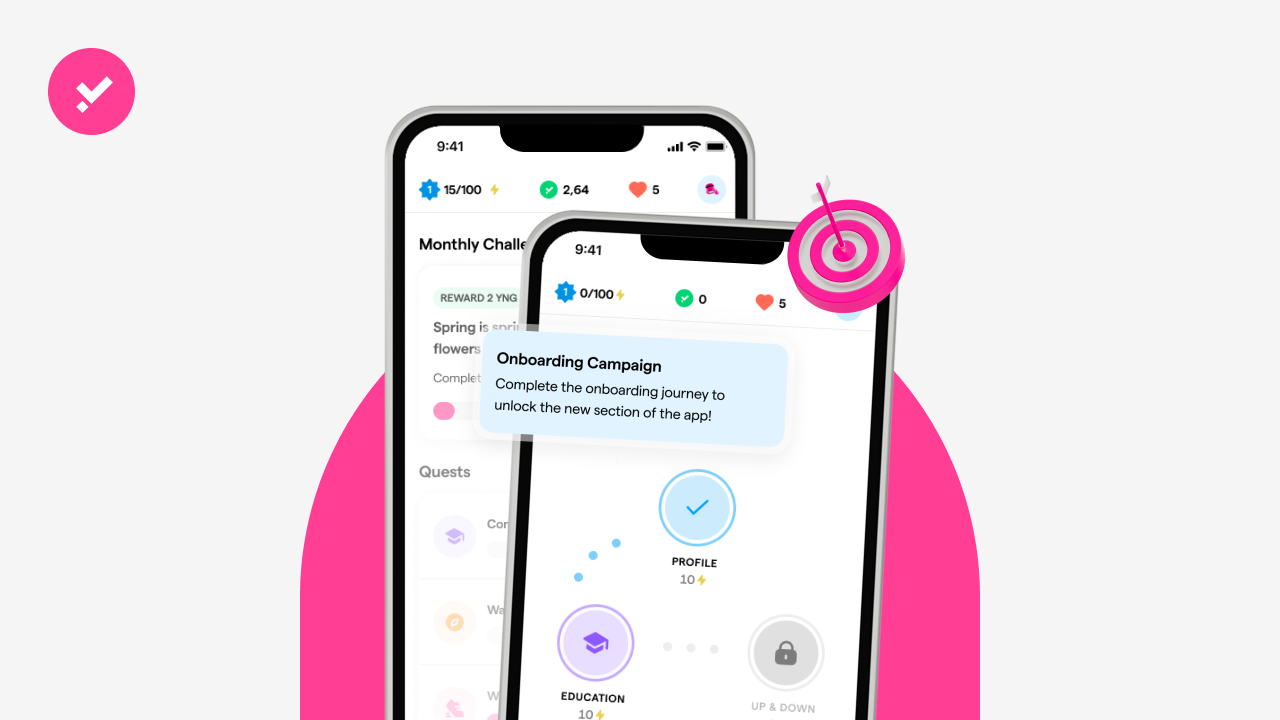
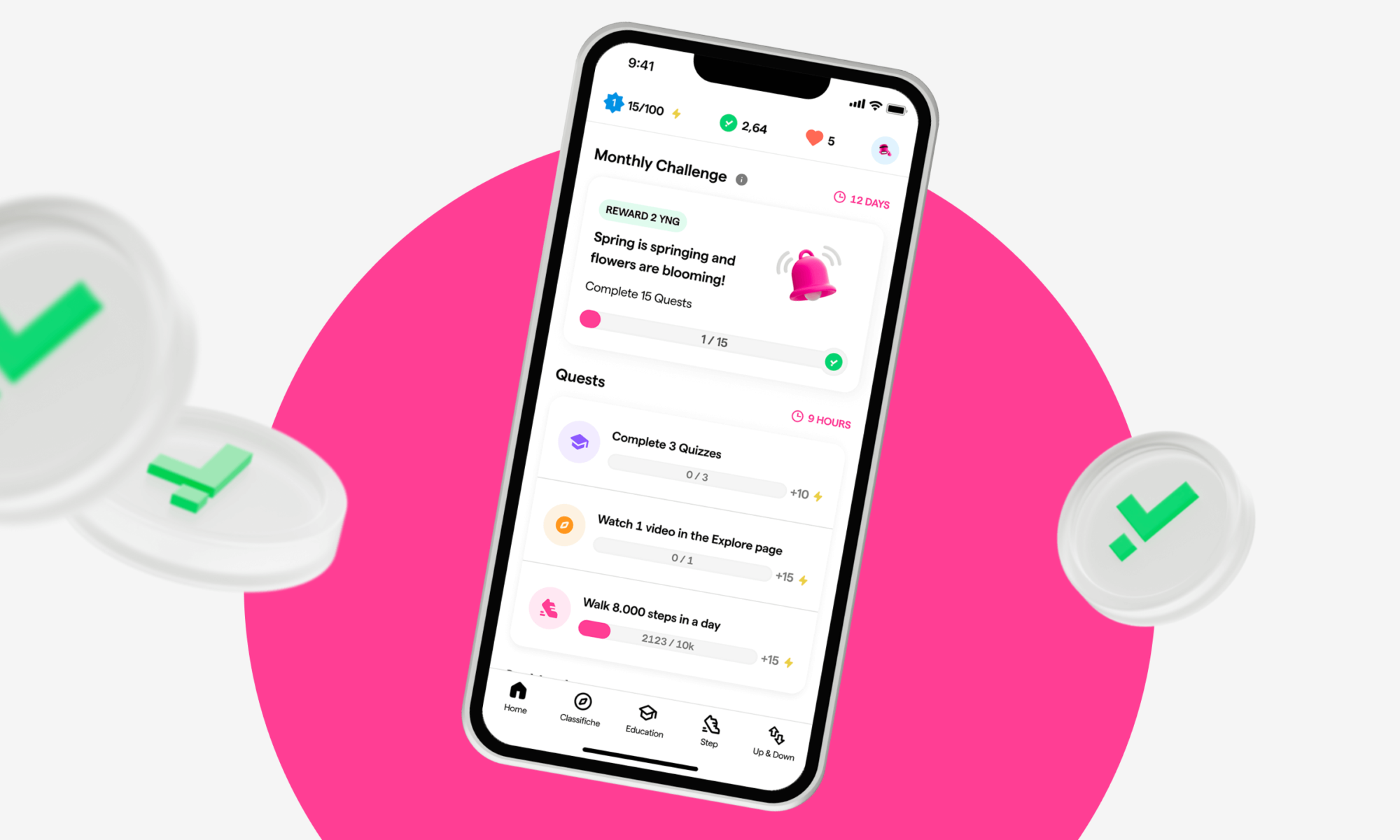
1. Quests
In the Step Home, you can find Quests related to each feature, each with a different colour. Quests allow you to earn experience points every day: check the deadline, and use the features to complete them and redeem XP.
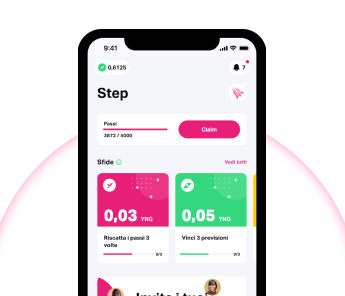
2. Claim
Young Platform Step counts all your steps (if connected to Google Fit or Health). In the ‘Step’ section, with the ‘Claim’ button, you can redeem and accumulate them to participate in the step quests in the Home (you recognise them because they are the ones in yellow). The fuchsia quests, on the other hand, do not count steps but all the times you redeem them. Remember to redeem the steps every time you accumulate 4,000 steps, otherwise the count will stop.
3. Rankings
In the ‘Steps’ section of the app you will find step rankings! The challenge is to beat other users in the community at who can accumulate the most steps in an interval of time. You can join an existing ranking or create one: each one has a limited duration and number of places. To participate, you have to pay a small share of your YNG and the sum of the shares of all participants will be distributed to the winners. Furthermore, the more rankings you win, the more you progress in the blue quests.
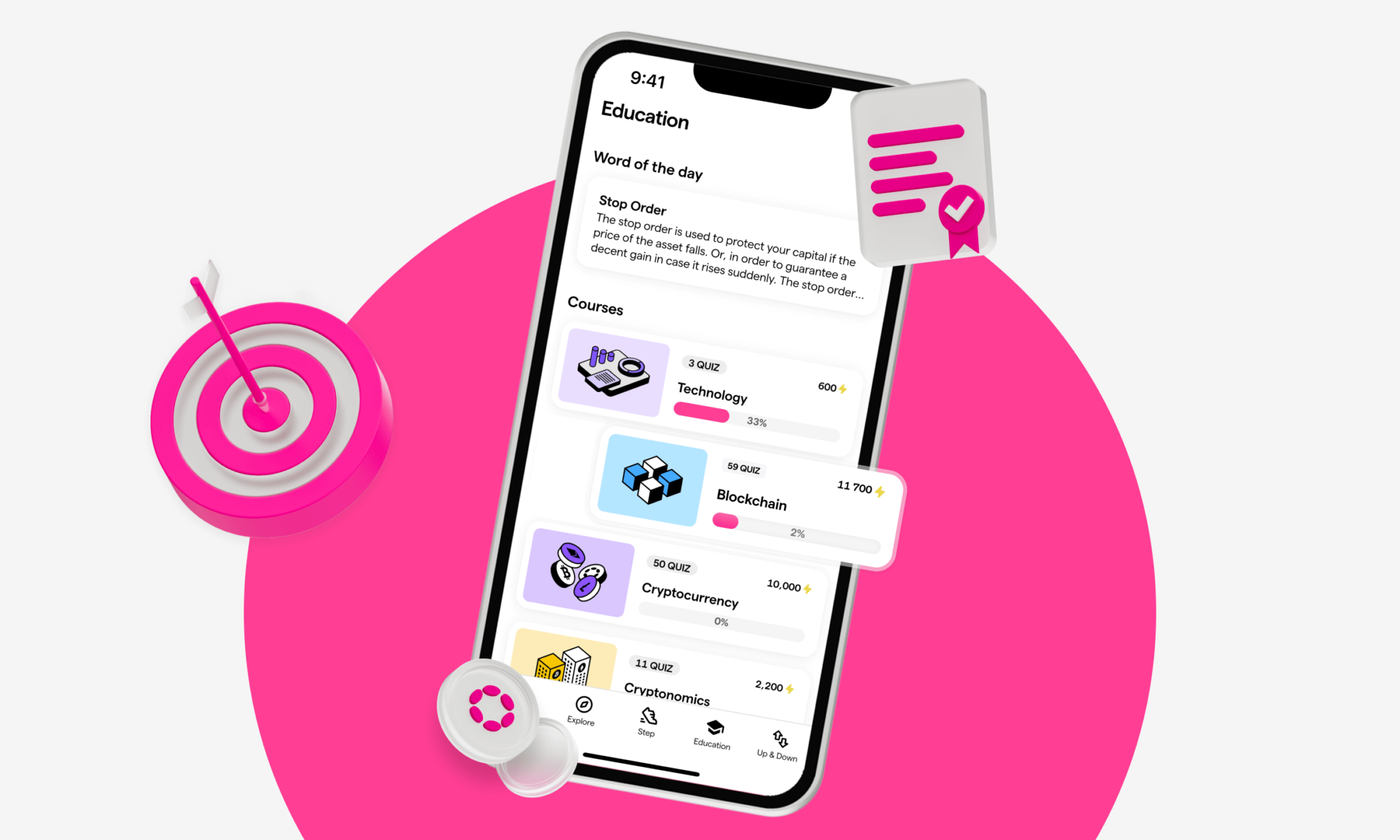
4. Quizzes
On Young Platform Step, in the Education section, you can learn everything about the crypto world, from the basics to the more advanced aspects thanks to specific Young Platform Academy articles divided into 6 categories:
- Blockchain to learn what the underlying cryptocurrency technology is and how it works;
- Cryptoeconomics to discover the specific features and characteristics of the crypto economy;
- Cryptocurrencies to delve into which are the main ones on the market, from their tokenomics to their uses;
- Crypto Heroes to get up close and personal with the protagonists of the crypto world, from Vitalik Buterin to the mysterious Satoshi Nakamoto;
- Easy Economics to explore basic economic concepts;
- Trading to learn about the theory and practice of this activity.
But how does it work and what is Education on Young Platform Step? Simple: each article is associated with a quiz that allows you to gain XP if you guess the correct answers. NB: To take the quiz, you have to spend one life and are given 5 lives by default.
When you run out of lives, you can recover them by waiting for the indicated time, or by watching one of the advertising videos, or even with the Unlimited lives boost (explained below).
Step is also your one-stop shop for the latest news and updates from the crypto world, selected for you day by day directly from the Young Platform Blog.
4. Up&Down
In the Up&Down section you can try to guess whether the price of a crypto will go down (down) or up (up) by choosing a time interval between 3, 6 or 12 hours.
Every time you place a forecast you consume a life, like for Quizzes.
For each right forecast you gain XP, the wider the time interval you choose, the greater the number of XP.
Step counts all your correct forecasts advancing in the green quests. Put your market knowledge to the test!
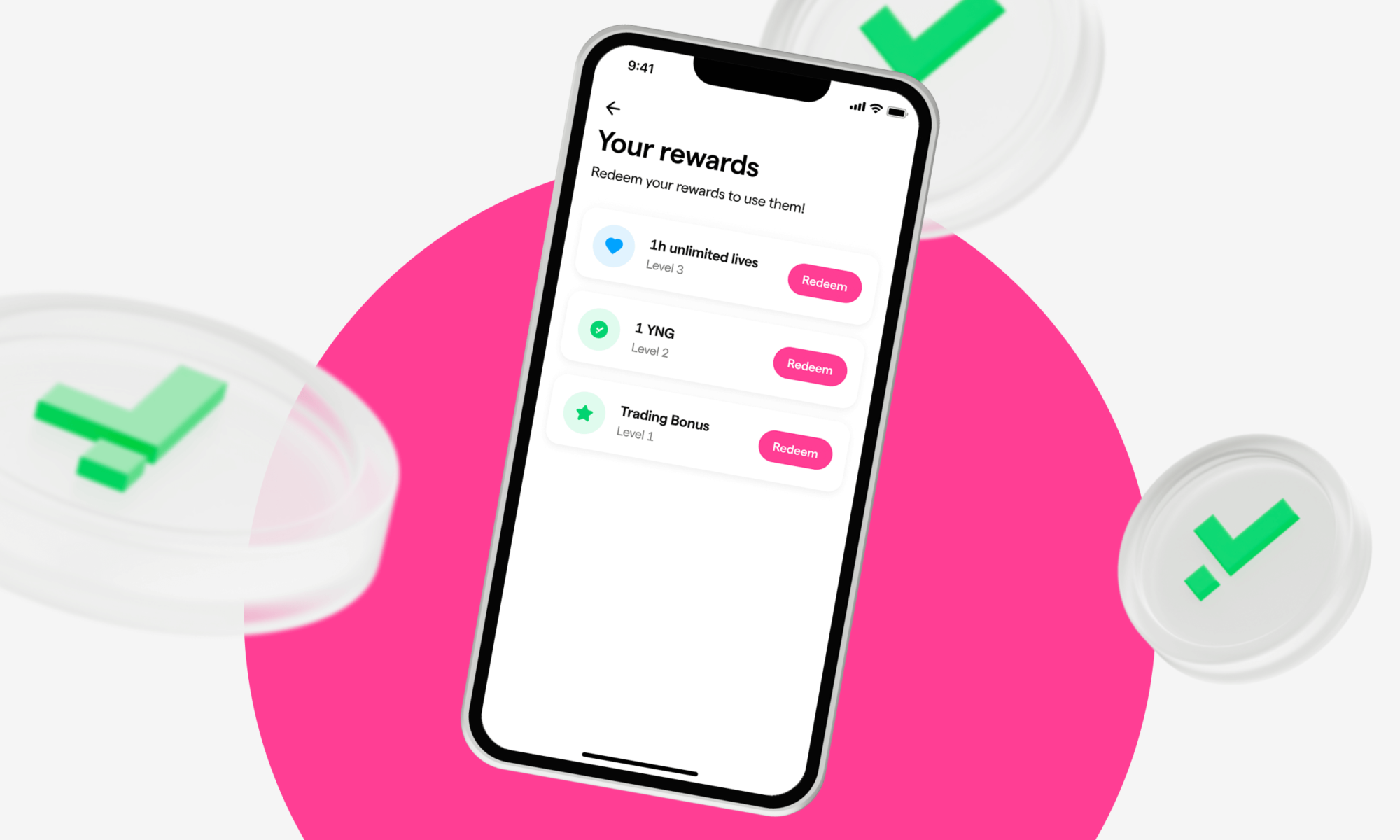
What is Unlimited Lives and how does it work?
On Young Platform Step the Unlimited Lives is the life boost that allows you not to lose any lives for 1 hour. You can then use it to do more than 5 Quizzes or more than 5 Forecasts in a row.
To get it, just go to the top bar where the lives icon is, click on it and select ‘Get unlimited lives’ to buy it for 1YNG.
Alternatively, you can obtain it upon reaching certain Levels: check when you’ll receive Unlimited lives by selecting the Level icon in the top bar and clicking on ‘Show Levels’.
Once you have the boost, you have to redeem it to activate it and use it.
The Marketplace
On Young Platform Step you can also find the Marketplace, which allows you to receive cashback in YNG of up to 20% on purchases from selected shops such as Nike, Guess or Decathlon.
The Profile
Your progress is easily visible in the top bar of the app, but if you enter your Profile it’s a whole different story. Your Level, Available Lives, YNG received and XP accumulated are easily viewable, and over time your personal section will become more and more detailed and full of victories. Choose from the Avatars available to customise your profile!
How to transfer YNG to Young Platform
Here’s what Step is and how it works: by playing and levelling up you get your first YNGs, which will accompany you into the real crypto market.
So, once you’ve completed your levels and obtained the minimum amount of YNG, you can transfer them to the Young Platform app and get benefits by joining Clubs or use them for buying and selling. Young Platform is in fact an exchange where you can buy and sell major cryptocurrencies. To transfer YNG from Step to the exchange you need to link the two accounts, complete a minimum deposit of 20 Euro and a minimum crypto trade of 20 Euro. The next day you can create a gift card from Step and send the tokens to Young Platform. You can find the process explained in detail here.
To learn more about what Young Platform Step is and how it works, check out all the dedicated Support Guides.

Sign up to Step!