Japan, Prime Minister Shigeru Ishiba has resigned. Sanae Takaichi has been nominated in his place. The issue deserves a focus. Why?
Japan, at this moment, deserves a deeper look. Here we will deal with a new figure in Japanese politics, Sanae Takaichi, a possible future Prime Minister, especially due to her ideas on economic policy. Let us not forget, in fact, that Japan is the fourth-largest economy in the world, with significant weight globally.
Japan: Let’s Quickly Give Some Context
In early September, Japan experienced a delicate moment regarding national politics: Prime Minister Shigeru Ishiba, leader of the Liberal Democratic Party (LDP), resigned.
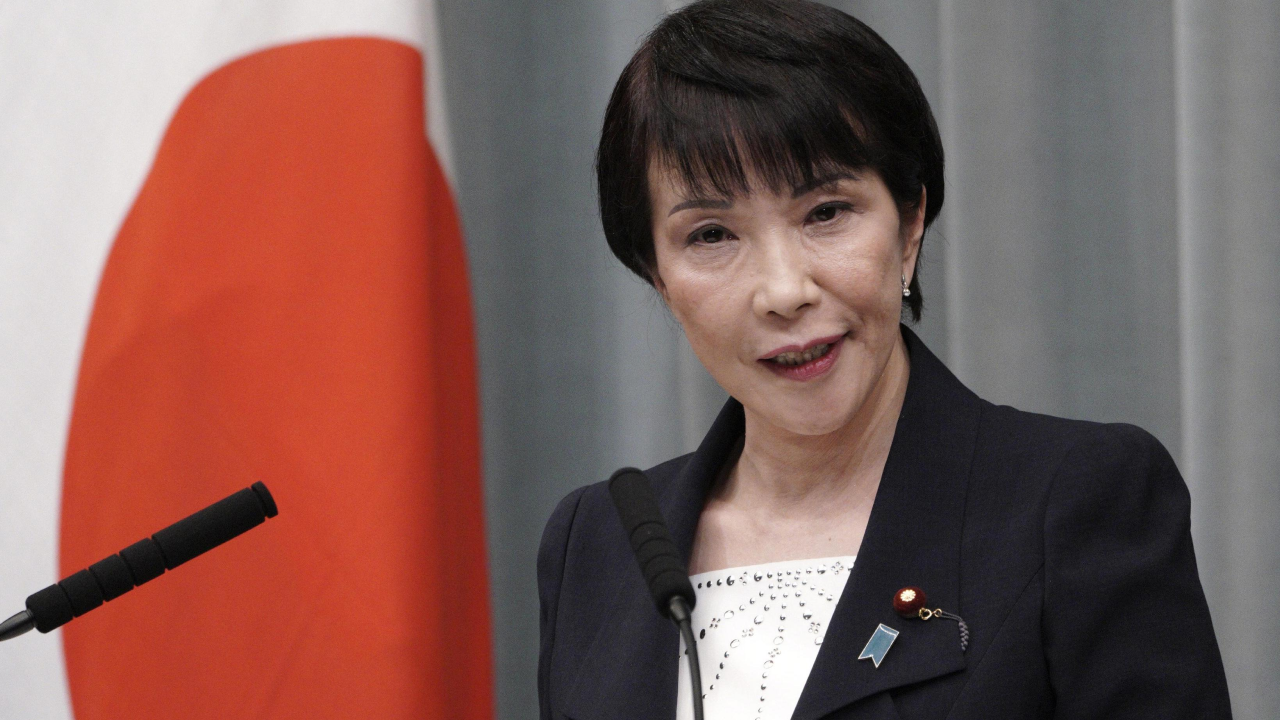
The LDP members chose Sanae Takaichi in his place, who could be the first woman in Japan to hold the role of Prime Minister. First, however, the LDP must find one or more partners with whom to form the coalition that will govern the country. This is because Komeito, literally the “Clean Government Party”, which for more than twenty years was a government ally with the LDP, declared it wanted to break the agreement. All this will make Takaichi’s nomination as Prime Minister slightly more complex.
Let us now see, in more detail, who Sanae Takaichi is and why these political dynamics should interest us.
Who is Sanae Takaichi?
The daughter of an office worker and a policewoman, Sanae Takaichi was born in Nara Prefecture in 1961. Before entering politics, Takaichi was a heavy metal drummer, an expert diver, and a television presenter.
She developed an interest in politics around the 1980s and entered the political game in 1992, when she tried to run for parliament as an independent. The attempt failed, but she did not give up: four years later she ran again with the LDP and was elected. From that moment she is considered one of the most conservative figures of the Liberal Democratic Party.
Moving on to her positions on economic policy, Takaichi is an absolute fan of Margaret Thatcher. Her goal, as she herself has declared, is to become the Iron Lady – the nickname given to Thatcher when she governed – of Japan. Furthermore, she was a protégé of former Japanese Premier Shinzo Abe, a very influential figure in her formation.
This last point is very important: Shinzo Abe, in fact, was the author and strong supporter of an economic policy based on a strong injection of money through fiscal stimuli and increased public spending. The aim was to revitalise the Japanese economy, at that moment in a deep crisis caused also by the shock of the 2008 financial crisis.
Specifically, Abenomics – a portmanteau of Abe and Economics – was founded on three arrows: expansive monetary policy to increase inflation (Japan was in a state of chronic deflation) and depreciate the Japanese Yen, favouring national exports; negative interest rates to incentivise money circulation in the economy; and structural reforms to increase Japan’s competitiveness. Sanae Takaichi has promised to relaunch her vision of Abenomics.
Let us therefore come to the central core of the article.
With Sanae Takaichi, Japan Could Join the Fiscal Stimulus Club
The Japanese Iron Lady seems to have clear ideas: “I have never denied the need for fiscal consolidation, which is naturally important. But the most important thing is growth. I will make Japan a vigorous land of the Rising Sun again”. In other words, economic growth comes before balancing public accounts.
Sanae Takaichi, indeed, has promised huge public funding for government-led initiatives in sectors such as artificial intelligence, semiconductors, and batteries. She then declared she wants to increase defence spending and announced new tax credits – i.e., fiscal bonuses – to increase workers’ net income, deductions for domestic services, and other tax breaks for companies offering internal childcare services. Finally, her programme envisages strong public investments in infrastructure.
Financial markets, naturally, like all this very much: fiscal stimuli and expansive policy are manna from heaven for businesses, which can access credit more easily, invest, innovate and, ultimately, increase profits, with more than positive consequences for share values. And the effects have already been felt.
Market Reactions: The “Takaichi Trade”
The Nikkei, the main Japanese stock index, proved particularly sensitive to developments regarding Takaichi’s nomination as Prime Minister. Retracing the sequence of events, it is patently obvious how the Japan 225 – another name for the Nikkei – strongly desires the Iron Lady governing the Land of the Rising Sun.
For example, Sanae Takaichi was chosen by the LDP as heir to the resigning Prime Minister Ishiba on the weekend of October 4th and 5th, with stock exchanges closed. On Monday the 6th, the Nikkei gained more than 5.5% in a single session – reaching up to 8% if we also count Friday the 3rd, when rumours were already starting to circulate. The “Takaichi trade”, in this sense, led the main Japanese index to touch new highs.
Equally but conversely, when Komeito broke away from the coalition, undermining Takaichi’s nomination, the market reacted very negatively: on October 10th, the Nikkei lost more than 5.6% on the stock exchange.
Since Komeito’s renunciation, Sanae Takaichi has moved to look for other parties that could support the government alliance, obtaining good results. As favourable news came out, the Nikkei reacted consistently: +5.4% in the week between Monday the 13th and Friday the 17th of October.
Finally, on Monday, October 20th, the leader of the right-wing party Nippon Ishin – the Innovation Party – announced that he will make official the agreement to support Takaichi’s choice as Prime Minister. Once again, the Japanese index shows its appreciation: +2% in one session and an updated All Time High.
What is the Moral of the Story?
So, even the fourth economy in the world could start spending, and heavily. With the new leader, Japan could switch to a regime of great public spending, large deficits, and expansive monetary policy, enormously increasing public debt. The goal: to ensure that economic growth exceeds debt growth.
We are in a historical moment where the top three world economies, with the fourth trailing, have launched fiscal stimulus policies founded on a massive increase in public debt.
The moral, therefore, is singular and very simple: if the main thought is “spend”, the method to realise it is printing money. The necessary consequence is the devaluation of money – or, in other words, inflation. In similar scenarios, the main protection instruments, the so-called debasement hedges, have historically represented a valid exit route for capital preservation.
And when one speaks of debasement hedges, the mind immediately runs towards two assets: gold and Bitcoin. All this is even more valid if we rethink the very recent statements of Larry Fink, CEO of BlackRock, released during an interview with the broadcaster CBS: “Markets teach you that you must always question your convictions. Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies have a role, just like gold: they represent an alternative”.
What awaits us in the near future? If you don’t know how to answer, don’t worry, nobody knows. However, to not miss updates, you could subscribe to our Telegram channel and Young Platform, given that we deal often and very willingly with these themes.The information reported above is for exclusively informative and divulgative purposes. It does not in any way constitute financial advice, investment solicitation, or personalised recommendation pursuant to current legislation. Before making any investment decision or asset allocation, it is advisable to contact a qualified consultant.